
Cataracts
Solasta Healthcare is the guiding light in ophthalmology patient care.
The growing demands of an ageing population and associated visual impairment disease provided an opportunity to establish a world-class facility combining the highest quality patient care and safety with truly personalised treatments, undertaken by the most experienced consultant surgeons.
What is a Cataract?
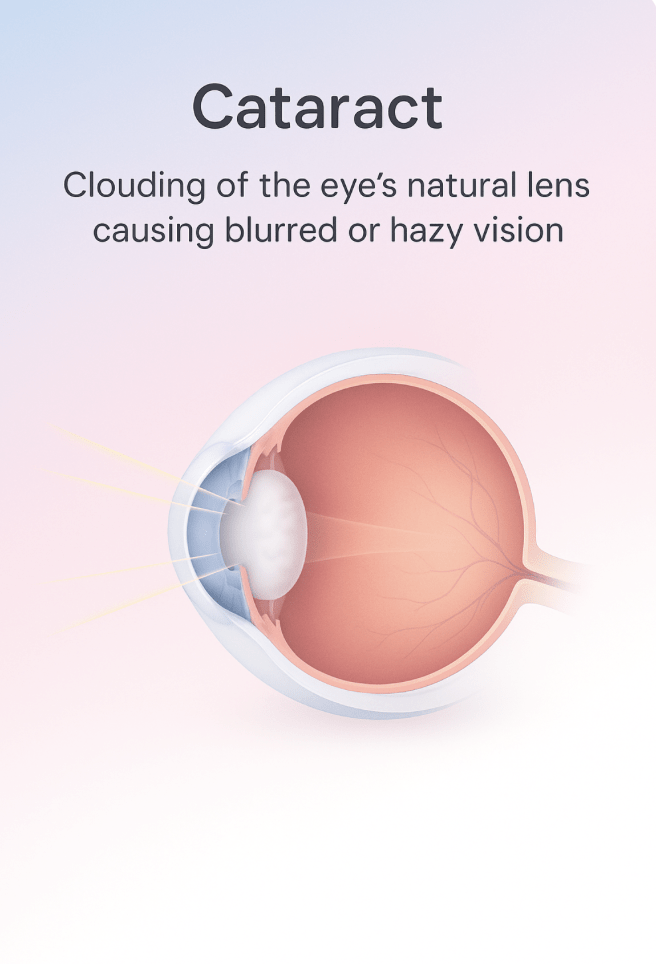
A cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye. The lens is usually clear, like glass. Over time (or sometimes due to injury, medication, or other eye conditions), proteins in the lens clump together.
This causes the lens to become cloudy, making it harder for light to pass through properly — resulting in blurred or hazy vision.
For people who have cataracts, seeing through cloudy lenses is like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window.
Most cataracts develop slowly and don't disturb eyesight early on. But with time, cataracts will eventually affect vision.
Cataract Symptoms
A slightly blurred vision is the most common early symptom of cataracts.
Apart from blurred vision, cataracts cause difficulty with glare (in bright sunlight or vehicle headlights when driving at night), dull colour vision, difficulty with reading and near vision, and frequent changes in spectacles prescription.
Initially, a change in glasses may help when vision begins to change from an early cataract. However, stronger glasses or contact lenses will no longer improve the vision as the cataract develops and becomes more dense and cloudy.
Over time theses symptoms can lead to feelings of anxiety, fear and sadness in some.
Not all people with cataracts will suffer the same symptoms. You may only experience one or two symptoms as cataracts develop and symptoms will progress over time. Once you identify a symptom your should book an appointment with a medical profession at your earliest convenience.

Cataract Diagnosis
Cataracts are typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination performed by an eye care professional, such as an optometrist or ophthalmologist. The diagnostic process may involve the following steps:
1. Medical History: The eye care professional will begin by discussing your medical history, including any symptoms you may be experiencing, such as blurry vision, difficulty seeing in low light, or increased sensitivity to glare.
2. Visual Acuity Test: This test measures your ability to see clearly at various distances using an eye chart. It helps determine the extent of your visual impairment.
3. Slit Lamp Examination: A specialised microscope used to examine the structures of your eye. By using a high-intensity light source and magnification, it can detect signs of cataracts, such as cloudiness or opacity in the lens.
4. Retinal Examination: This involves the examination of the back of the eye using an ophthalmoscope or other specialised instruments. It helps rule out other potential causes of vision problems and assesses the overall health of your eyes.
5. Refraction Test: This test measures the refractive error of your eyes, which determines the prescription needed for glasses or contact lenses. It helps determine if any other visual impairments are present alongside cataracts.
Based on the results of these tests, the eye care professional can diagnose cataracts and determine the appropriate course of treatment. They will also consider factors such as the severity of the cataracts, impact on vision, and your overall eye health in developing a treatment plan tailored to your needs.

Cataract Treatment
During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens in the eye is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). For most patients, the treatment of choice is a painless minimally-invasive procedure, called phacoemulsification, which lasts around 15-20 minutes.
Cataract surgery isn’t painful as it’s carried out under local anaesthetic, which means you’ll be awake during the procedure. Your eyes are numbed using eye drops, so don’t worry – there are no needles or injections involved.
Using an operating microscope, your ophthalmic surgeon will make a very small incision in the surface of the eye in or near the cornea and then inserts a thin probe into the eye.
The ultrasound probe uses ultrasonic vibrations to dissolve the clouded lens into tiny fragments that are then gently removed through the same ultrasound probe. An artificial lens is placed into the space that the original lens previously occupied. This lens is required to help your eye focus following cataract surgery.
After the surgery, you will be moved to a recovery area, where the medical staff will monitor your condition for a short period. You may receive eye drops or medications to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. You will be given postoperative instructions to follow at home.
Most people experience improved vision shortly after the surgery, although it may take a few weeks for the vision to stabilize and fully adjust to the new intraocular lens.
Cataract surgery recovery
You will spend a short period of time resting in the outpatient recovery area before you are ready to go home. You will need to have someone drive you home.
Following your surgery, it is very important to put in the eye drops exactly as prescribed by your ophthalmologist to promote healing. You will also need to take care to protect your eye by wearing the eye shield whenever you sleep. Be sure not to rub your eye. The first day of your recovery, you must avoid strenuous activity such as exercise or bending and heavy lifting.
Avoid getting any water, dirt or dust in your eye, which can lead to infection.
After 3-4 days, you can get back to your normal activity. You may have some blurry vision a few days to weeks after surgery procedure. If you experience any pain or loss of vision, be sure to call your ophthalmologist.

